Democracy is a form of government that gives people the right to choose people to represent them and their interests as well as being involved in the civic process. The key components that define democracy are free and fair elections, equality, and protection of rights and liberties , such as freedom of speech and religion, for all people.
There are multiple variations of democracy since democracy has a broad range.
Direct versus representative democracy
Direct democracy is when the people directly meet and vote on issues pertaining to their interests. Instead of electing people to make decisions, the people make those decisions directly. Examples include initiative, recall, and referendum.
Initiatives allow voters and the people to pass laws that they are passionate about whereas referendum results in interaction with the legislature and the community in approving or rejecting legislation. When voting comes along, people can vote on propositions that people or the legislature proposes. Recall is when people are unhappy with the elected officials, so they can petition and remove them from office.
Representative democracy is electing individuals to represent our interests, which is known as a republic.
Federal versus Unitary democracy
Federal democracy is all about protecting the rights of individual states or political units in a larger country. These political units have their own laws and government separate from the national government, and the national government does not have the right to interfere with the laws unless they confront the state government. An example of this would be the United States. There are 50 states that have their own laws, but they still follow the national government.
Unitary democracy consists of one central power, which is the national government. There are presence of political units, but they administer the laws and do the work that the central government enacts and calls for. An example of this would be Great Britain.
There are multiple variations of democracy since democracy has a broad range.
Direct versus representative democracy
Direct democracy is when the people directly meet and vote on issues pertaining to their interests. Instead of electing people to make decisions, the people make those decisions directly. Examples include initiative, recall, and referendum.
Initiatives allow voters and the people to pass laws that they are passionate about whereas referendum results in interaction with the legislature and the community in approving or rejecting legislation. When voting comes along, people can vote on propositions that people or the legislature proposes. Recall is when people are unhappy with the elected officials, so they can petition and remove them from office.
Representative democracy is electing individuals to represent our interests, which is known as a republic.
Federal versus Unitary democracy
Federal democracy is all about protecting the rights of individual states or political units in a larger country. These political units have their own laws and government separate from the national government, and the national government does not have the right to interfere with the laws unless they confront the state government. An example of this would be the United States. There are 50 states that have their own laws, but they still follow the national government.
Unitary democracy consists of one central power, which is the national government. There are presence of political units, but they administer the laws and do the work that the central government enacts and calls for. An example of this would be Great Britain.
Democracy first originated in ancient Athens. Athenian democracy was one of the earliest forms of democracy. Voters and the people directly voted on laws, rather than choosing politicians to vote and craft legislation. Romans developed the Senate, which consisted of people who advised the king.
In 930, Vikings were known to create the first legislative assembly, presently known as the Parliament. They called it the Althing, but it basically brought people together to discuss issues in their community and find solutions to those problems.
As cities began to develop in the Middle Ages, city-states were created to help govern and control the social and economic life of the people. Cities in Italy elected people to serve in councils. This did not last that long because several city states were going into wars with other city-states over land and power. Later on, the nation-state was created to unify cities together and have a strong government. In England, the creation of the Parliament marked the advancement of representative democracy. The purpose of the Parliament was to represent the people and check the power of the monarchy.
In 18th century Europe, improvements were being made in people participating in democracy. Previously it used to be upper class men who could serve and vote in several European countries, but universal male suffrage was given to all men, regardless of their class. However, women still did not have the right to vote.
Europeans principles of democracy and representation spread to America in which the Founders, who recently achieved independence from Britain in 1776, were creating the constitution. They wanted to have a government that represents the people. Thus, the three branches of government were created as well as defining the election process on how to choose the president. Even before achieving independence, American colonists were known for establishing representative governments long before the creation of the constitution. Town halls in New England brought people together to talk about issues, and the colonial governors and councils were elected by the people.
Later on throughout the years, suffrage has been granted to several populations, such as people of color, women, and other minorities.
20th century hits, and results in several countries shifting to democracy. With facism in Italy and Germany and military dictatorships in Latin America, these ideologies had a heavy damage onto the government and its institutions. These leaders in those regions took full control over the people and wanted to advance their interests rather than caring about the people.
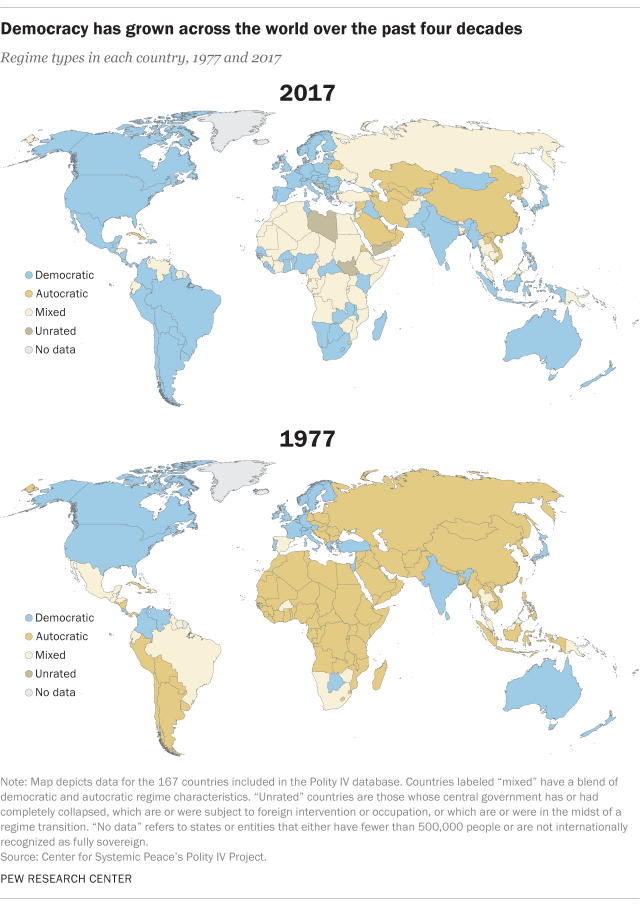
Today, according to Pew Research, 96 out of 167 countries with populations of at least 500,000 (57%) had some form of democracy. With the end of colonization and wars, several countries shifted to democracy in order to represent the community and the people.
In 930, Vikings were known to create the first legislative assembly, presently known as the Parliament. They called it the Althing, but it basically brought people together to discuss issues in their community and find solutions to those problems.
As cities began to develop in the Middle Ages, city-states were created to help govern and control the social and economic life of the people. Cities in Italy elected people to serve in councils. This did not last that long because several city states were going into wars with other city-states over land and power. Later on, the nation-state was created to unify cities together and have a strong government. In England, the creation of the Parliament marked the advancement of representative democracy. The purpose of the Parliament was to represent the people and check the power of the monarchy.
In 18th century Europe, improvements were being made in people participating in democracy. Previously it used to be upper class men who could serve and vote in several European countries, but universal male suffrage was given to all men, regardless of their class. However, women still did not have the right to vote.
Europeans principles of democracy and representation spread to America in which the Founders, who recently achieved independence from Britain in 1776, were creating the constitution. They wanted to have a government that represents the people. Thus, the three branches of government were created as well as defining the election process on how to choose the president. Even before achieving independence, American colonists were known for establishing representative governments long before the creation of the constitution. Town halls in New England brought people together to talk about issues, and the colonial governors and councils were elected by the people.
Later on throughout the years, suffrage has been granted to several populations, such as people of color, women, and other minorities.
20th century hits, and results in several countries shifting to democracy. With facism in Italy and Germany and military dictatorships in Latin America, these ideologies had a heavy damage onto the government and its institutions. These leaders in those regions took full control over the people and wanted to advance their interests rather than caring about the people.
Today, according to Pew Research, 96 out of 167 countries with populations of at least 500,000 (57%) had some form of democracy. With the end of colonization and wars, several countries shifted to democracy in order to represent the community and the people.
RESOURCES FOR EDUCATORS
| democracy.pdf | |
| File Size: | 6206 kb |
| File Type: | |